Confocal microscopy can be considered a bridge between these two classical methodologies.
Advantages and disadvantages of laser scanning confocal microscopes.
A thick 16 micrometer section of fluorescently stained.
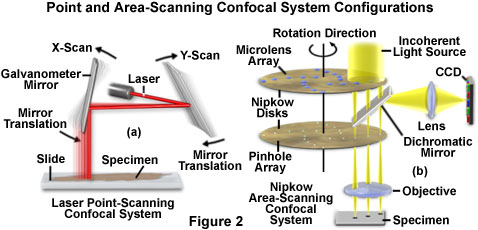
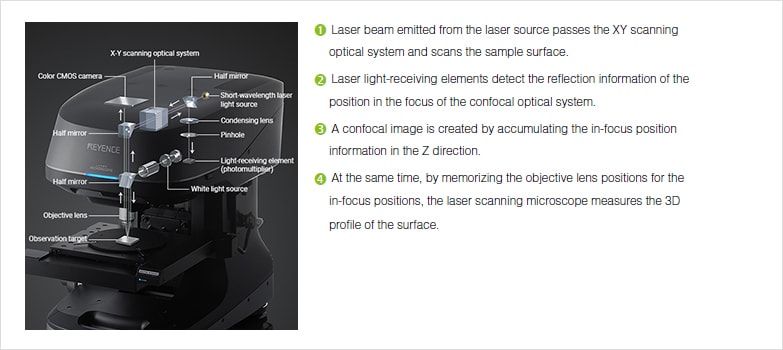
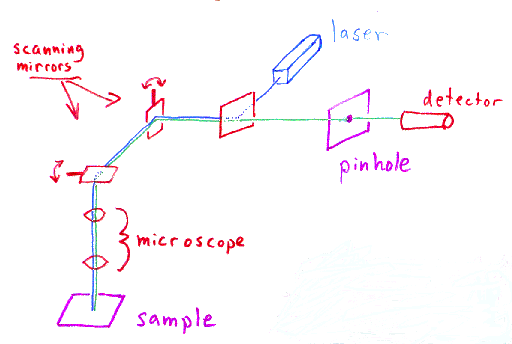
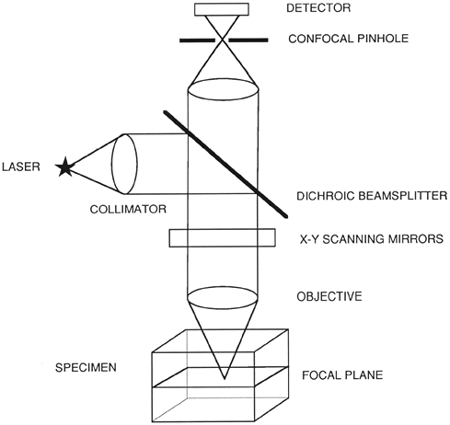
The confocal principle in epi fluorescence laser scanning microscopy is diagrammatically presented in figure 2.
Comparing to a wide field detection taking a snapshot of.
Can produce 3d.
It provides the ability to collect sharply defined optical sections from which three dimensional renderings can be created.
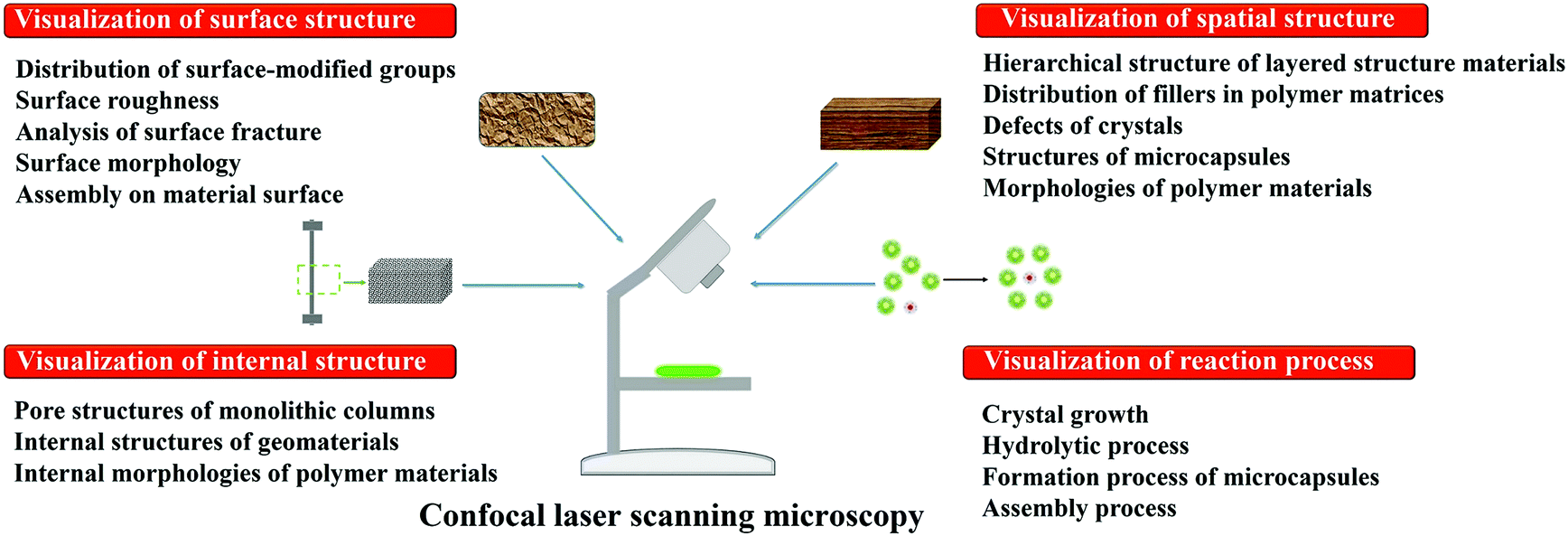
Advantages of confocal laser scanning microscopy industrial applications of confocal microscopy thin film profiling.
The many advantages confocal microscopy provides over conventional widefield microscopy for life sciences applications helps researchers observe the internal.
The primary advantage of laser scanning confocal microscopy is the ability to serially produce thin 0 5 to 1 5 micrometer optical sections through fluorescent specimens that have a thickness ranging up to 50 micrometers or more.
Where electrons are used to form images.
The benefits of delivering higher efficiency imaging at lower laser powers include less photobleaching phototoxicity and is less expensive than confocal laser scanning microscopes.
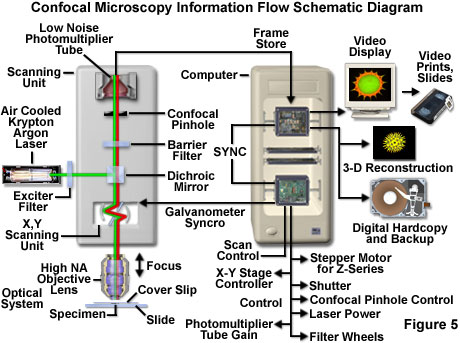
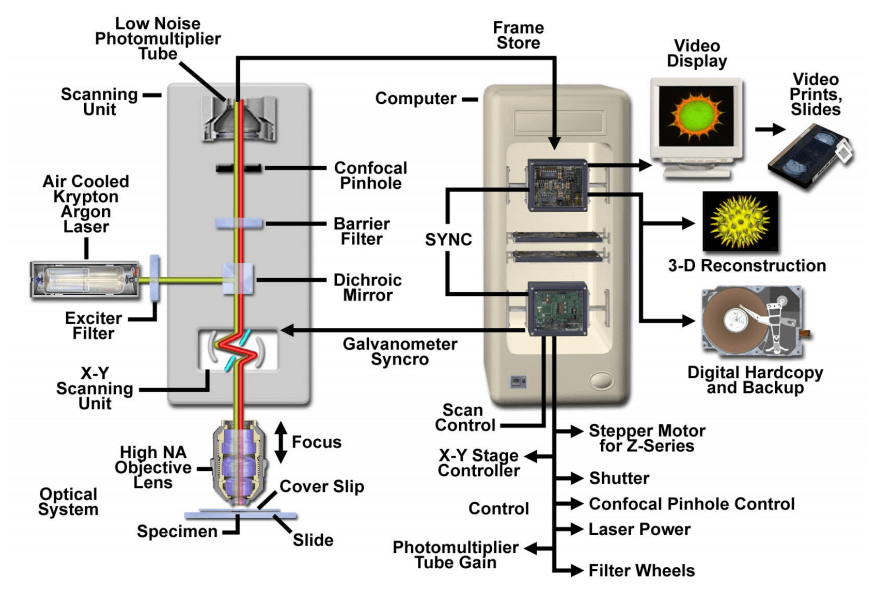
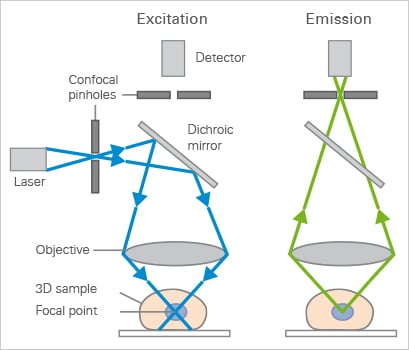
Coherent light emitted by the laser system excitation source passes through a pinhole aperture that is situated in a conjugate plane confocal with a scanning point on the specimen and a.
Confocal is a powerful tool but it does have some limitations.
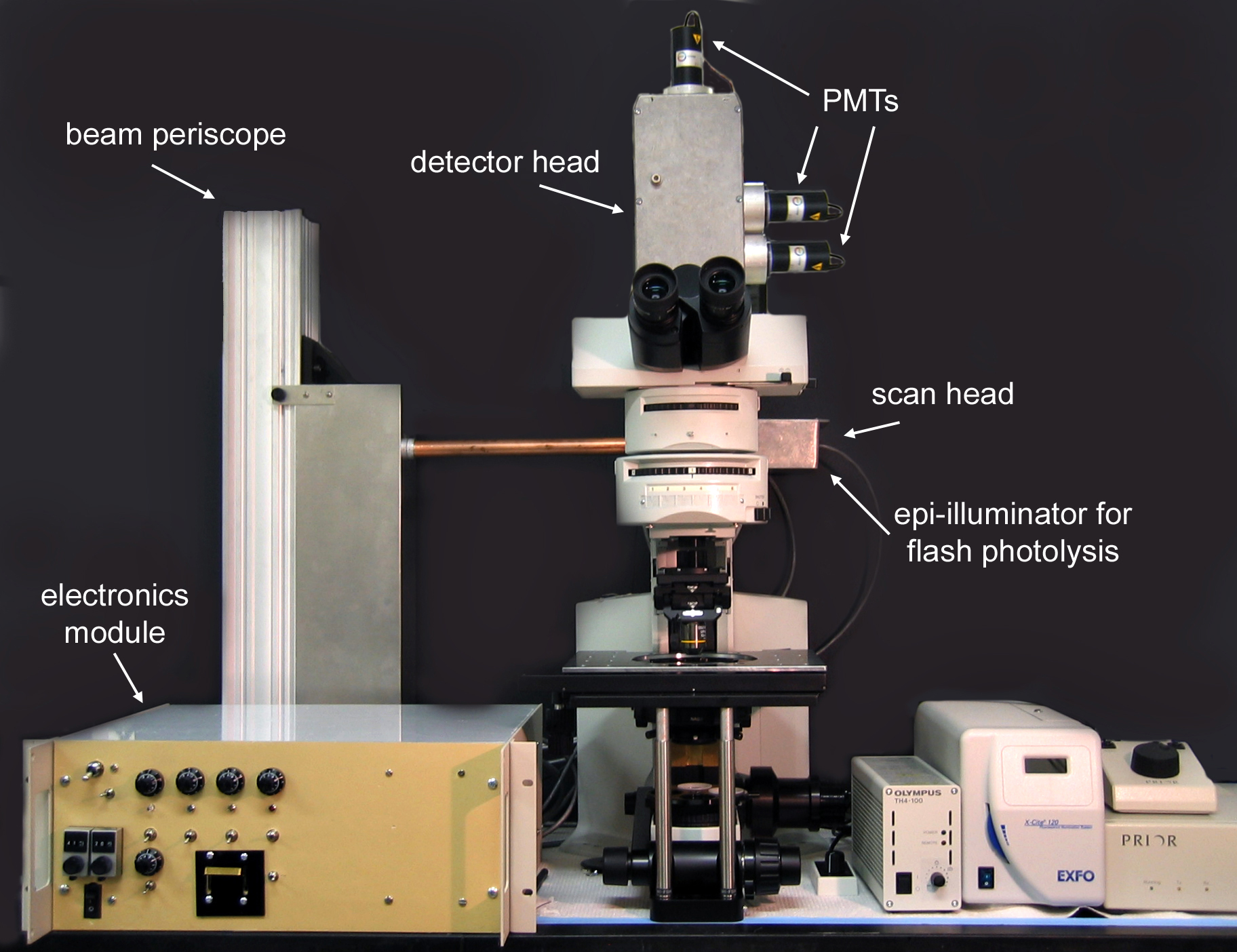
Laser scanning confocal microscope.
Advantages and disadvantages of confocal microscopy.
When investigating multilayer structures the true surface of a substrate can be observed through a surface coating.
Laser scanning confocal microscopy.
Illustrated in figure 1 are a series of images that compare selected viewfields in traditional widefield and laser scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy.
The two main types of confocal microscopes are the laser scanning microscopes and the tandem scanning microscopes tsm.
Electrons are reflected off the specimen to produce a 3d image.
The former is ideal for immunofluorescence microscopy and the latter is.
Speed a typical confocal uses raster scanning which means it scans the specimen point by point.
Confocal microscopy offers several advantages over conventional optical microscopy including controllable depth of field the elimination of image degrading out of focus information and the ability to collect serial optical sections from thick specimens.
Here are 3 quick ones.